Definition: An application server, or appserver, is software that
typically interfaces one or more databases to convey processed data to and from
a user interface.
The user interface is often web based through a browser, but it may be through
other means to client computers in any distributed
network situation. The application server
and databases may be housed in the same or separate computers.
The term “server” is applied to computers in a number of ways: for instance
file, web and printer servers. “Application server” doesn’t necessarily apply
to a machine, however, as it is actually a piece of software. Loosely speaking,
any software that centrally processes
data for distributed client machines can be seen as an application server.
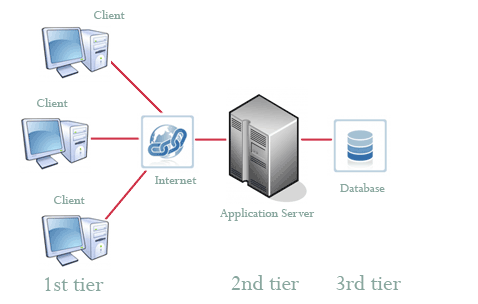
Interestingly, even though the three tiers are usually split across three
separate computers, it’s still possible for all three tiers of interface,
application, and database to sit on a single computer.
Advantages of Application Servers
Situating the application on a central computer decouples the clients from the
processing, allowing the client computers to access the application from any
platform. In other words, any Windows™ or Linux PC or Macintosh ® running any
browser can connect to a web based application server, regardless of their
individual specifications.
Centralisation of the application holds clear advantages for maintenance and
management. The computer that holds the application server can be maintained
and upgraded as required to meet demand, and the software can be engineered and
developed with a certainty of environment that wouldn’t be possible if the
processing had to be run on many distributed
computers.
Disadvantages of Application Servers
There are three main disadvantages of centralised processing. Firstly, if the
servers go down then clients simply can't access the application. Secondly, the
reliance on network connections, including the Internet, exposes the
vulnerability that any network outage also chokes all access to the
application. Finally, security, since data which may be sensitive could be
transferred over public networks.
The way to tackle the first two problems is to ensure adequate redundancy of
resources – so, backup
servers, network and Internet connections are a must. It’s almost
impossible to cover all angles in this, particularly as most of the WAN is out
of management control, and the steps taken to cover outage risk will be
governed by how mission critical the application server’s availability is.
Tackling security
issues is always difficult. However, there are a number of methods,
encryption and secure connections for instance, that are applied across all
forms of sensitive web interaction. These methods equally apply to application
server interfacing over the Internet.
Development Platforms
Java EE, once known as J2EE, is a platform that has become a benchmark for
application server developments. Not a standard as such, still compliance with
Java EE requirements grants a product significant value status. As a result,
Java is widely used as the language of choice for application servers.
However, Microsoft’s ASP.Net platform is also powerful and commonly used, and
many developers still use CGI and PERL. The choice of platform for an
application server may have technical constraints, and it is down to system
analysts and developers to make the choice of suitable solution.
Copyright © 2011 - All Rights Reserved - Softron.in
Template by Softron Technology